The 6 Best HIIT Exercises for All Skill Levels
The effectiveness of HIIT exercises can vary depending on individual preferences, abilities, and fitness objectives. Crafting a tailored routine that aligns with your needs is crucial for success.
HIIT, characterized by alternating brief bursts of intense activity with short recovery periods, aims to elevate heart rate and maximize physical exertion. This method enhances endurance, strength, and cardiovascular fitness, while also positively impacting metabolism and blood pressure. Additionally, HIIT is associated with mood enhancement and stress reduction, contributing to overall well-being. Its time efficiency allows for customizable workouts to fit busy schedules.
For beginners or those favoring gentler workouts, starting with accessible yet effective exercises is recommended. Initiating with 2 to 3 weekly sessions lasting 20 to 30 minutes each, gradually increasing duration, frequency, and intensity over time, is advisable. Exercises can be structured based on either time durations or repetitions and sets. Safety precautions, such as including warm-up and cooldown routines, selecting exercises appropriate to one’s fitness level, and listening to one’s body, are essential.
Here are a few beginner-friendly HIIT exercises:
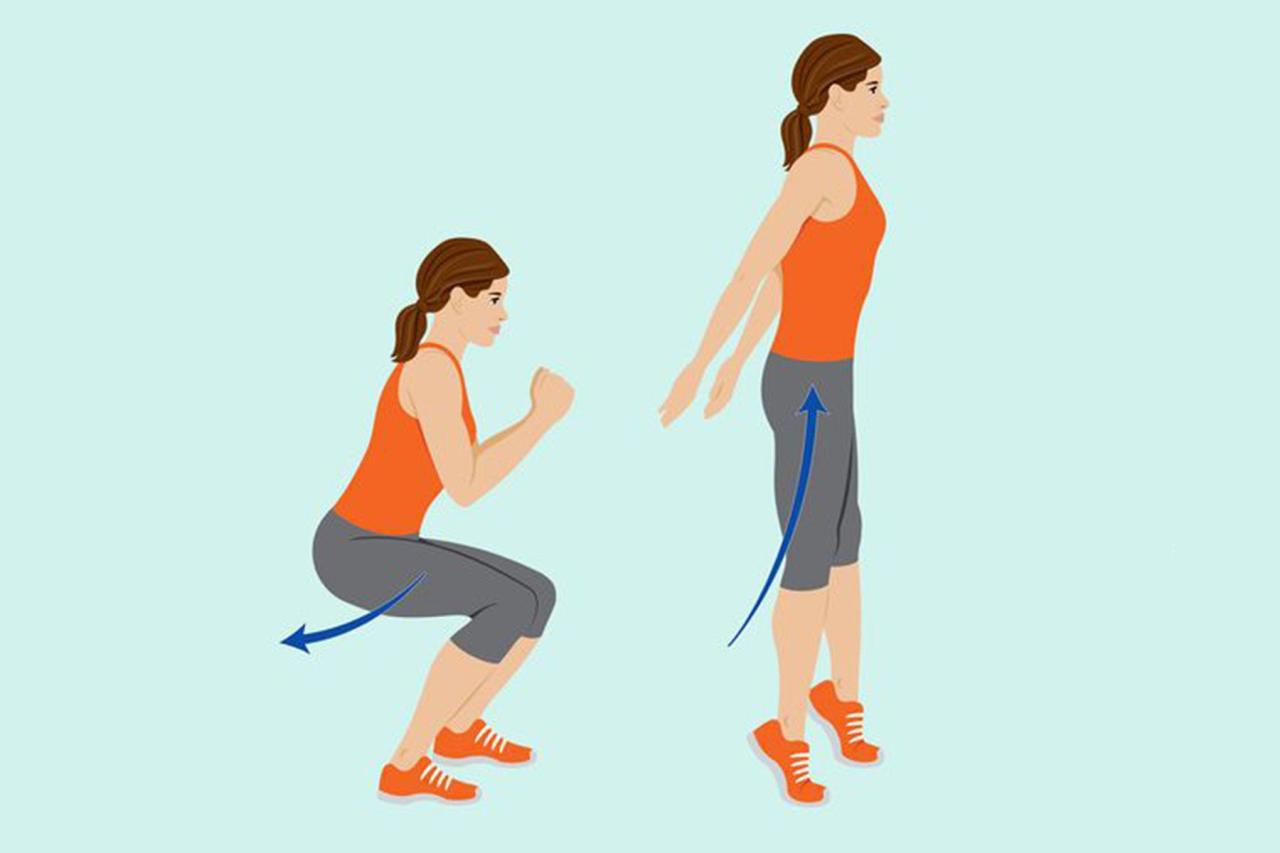
Bodyweight Squats
Stand with feet directly under shoulders.
Lower body slowly until thighs are parallel to the floor.
Press through heels to return to starting position.
Repeat movement.
Sprints
Sprint, then transition to walking or jogging. For added intensity, incorporate hill or stair sprints.
Once a foundation of strength and cardiovascular fitness is established, intermediate exercises can be introduced. Engaging in 2 to 4 weekly sessions lasting 25 to 45 minutes each is recommended. Intermediate exercises may include:
Mountain Climbers
Begin in plank position.
Alternate bringing left and right knees toward chest.
Kettlebell Swings
Stand with feet shoulder-width apart.
Bend at hips and slightly at knees.
Grab kettlebell handle with both hands.
Drive through hips, swinging kettlebell to chest level.
Lower kettlebell by hinging at hips.
Repeat motion fluidly.
For those seeking more advanced challenges, advanced HIIT exercises can be incorporated. Sessions typically last 45 to 60 minutes, with 4 to 5 sessions per week. Advanced exercises may include:
Clapping Push-ups
Start in plank position with hands slightly wider than shoulders.
Lower chest toward ground by bending elbows.
Push up forcefully, lifting hands off ground and clapping.
Land softly, returning hands to ground.
Repeat continuously.
Burpee Box Jumps
Begin standing in front of stable box.
Perform burpee by squatting down, placing hands on ground, and jumping feet back to plank position.
Do push-up, then jump feet back to hands.
Jump onto box, landing softly.
Stand upright on box.
Step down with control.
Add jump for increased difficulty.
Repeat sequence at steady pace.
In conclusion, HIIT offers an efficient workout method with potential benefits for weight management, heart health, and overall fitness. Consistency and gradual progression are key, along with prioritizing safety and making necessary modifications. As proficiency increases, exploring more challenging exercises can further enhance results.

The 12 Best Upper Body Exercises and 5 Workouts
Here’s an expert-curated list of the top upper body exercises and how to incorporate them into efficient workout routines. Whether you’re aiming to build muscle, enhance strength, or improve overall fitness, these exercises have you covered:
12 Top Upper Body Exercises
Overhead Press
Equipment Needed: Squat or power rack, barbell, weight plates, wrist wraps (optional)
Muscles Worked: Shoulders, triceps
Sets & Reps: 3-4 x 5-8
Description: The overhead press is a fundamental shoulder exercise, emphasizing strength and functionality. Whether using a barbell, dumbbells, or kettlebells, it’s a versatile movement for building shoulder strength and mobility.
Bench Press
Equipment Needed: Bench press station, barbell, weight plates, wrist wraps (optional)
Muscles Worked: Chest, shoulders, triceps
Sets & Reps: 3-4 x 6-10
Description: The bench press is a classic exercise for developing horizontal pressing strength, targeting the chest, shoulders, and triceps. Variations like incline, decline, or dumbbell presses offer versatility in training.
Bent-Over Barbell Row
Equipment Needed: Barbell, weight plates, lifting straps (optional), lifting belt (optional)
Muscles Worked: Lats, traps, lower back, biceps, core
Sets & Reps: 3 x 6-12
Description: The bent-over row strengthens the upper back and lats, promoting muscle mass and strength. It’s also beneficial for lower back stability and isometric strength.
Weighted Dip
Equipment Needed: Parallel bars, wrist wraps (optional), dip belt (optional)
Muscles Worked: Triceps, chest, shoulders
Sets & Reps: 3 x 8-12
Description: Weighted dips are effective for targeting the triceps and chest, offering a longer range of motion compared to many triceps exercises. They can be scaled with body weight or additional weight for progressive overload.
Chin-Up
Equipment Needed: Pull-up bar, dip belt (optional)
Muscles Worked: Lats, biceps, upper back
Sets & Reps: 3-4 x 10+
Description: Chin-ups are challenging but rewarding exercises for building upper body strength, particularly in the back and biceps. Variations like assisted or weighted chin-ups offer options for progression.
Push-Up
Equipment Needed: Exercise mat (optional)
Muscles Worked: Chest, shoulders, triceps
Sets & Reps: 2-3 x 10-20
Description: Push-ups are versatile bodyweight exercises that engage multiple upper body muscles, making them effective for building strength and endurance. Modifications like incline or decline push-ups cater to different fitness levels.
Lat Pulldown
Equipment Needed: Lat pulldown station, lifting straps (optional)
Muscles Worked: Lats, upper back, biceps
Sets & Reps: 2-3 x 10-15
Description: Lat pulldowns target the lats and upper back, offering a stable platform for heavy loading. Variations in grip width or attachments provide options for targeting different areas of the back.
Inverted Row
Equipment Needed: Barbell, squat rack, or stable horizontal bar
Muscles Worked: Lats, biceps, upper back, core, glutes
Sets & Reps: 2-3 x 10+
Description: Inverted rows are underrated exercises for upper back strength, offering scalability and minimal lower back involvement. Adjustments in bar height or adding weight can tailor the exercise to individual needs.
Overhead Triceps Extension
Equipment Needed: Adjustable cable station, attachment of choice
Muscles Worked: Triceps
Sets & Reps: 2 x 12-15
Description: Overhead triceps extensions isolate and strengthen the triceps, promoting arm mass and definition. Variations in grip and equipment offer versatility in training intensity.
Landmine Press
Equipment Needed: Landmine attachment, barbell, weight plates
Muscles Worked: Triceps, shoulders, core
Sets & Reps: 2 x 12-15
Description: The landmine press targets the upper body with less shoulder strain, making it suitable for individuals with mobility issues. It’s an effective exercise for building upper body strength and stability.
Farmer’s Carry
Equipment Needed: Dumbbells, kettlebells, or trap bar frame
Muscles Worked: Traps, upper back, lower back, core
Sets & Reps: 2 x 30 seconds
Description: Farmer’s carries are excellent for building upper body strength and endurance, as well as grip strength. They also provide a cardiovascular challenge, making them beneficial for overall conditioning.
Bicep Curls
Equipment Needed: Dumbbells or barbell
Muscles Worked: Biceps
Sets & Reps: 3 x 8-12
Description: Bicep curls isolate the biceps, promoting arm hypertrophy and strength. Variations in grip and equipment allow for targeted muscle engagement and progression.
Upper Body Workouts to Incorporate
Upper Body Warm-Up
This warm-up routine prepares the shoulders for upper body exercises, promoting mobility and stability.
Upper Body Workout for Muscle Growth
A muscle-focused workout targeting major upper body muscle groups for hypertrophy and strength gains.
Upper Body Workout for Strength
A strength-focused workout emphasizing heavy weights and low reps for maximal strength development.
Upper Body Workout for Men
Tailored to capitalize on male strength and muscle fiber composition, focusing on key upper body movements.
Upper Body Workout for Women
Adapted to suit female training preferences and potential advantages in higher-repetition training.
Bodyweight Upper Body Workout
A workout utilizing bodyweight exercises for strength and muscle building, suitable for beginners or those without access to equipment.
Benefits of Training Your Upper Body
Reduced Risk of Injury: Strengthening the upper body improves stability and reduces the risk of injury in daily activities.
Improved Performance: A strong upper body enhances performance in various exercises and activities, contributing to overall fitness and athleticism.
Muscle Balance: Training the upper body ensures balanced muscle development, improving posture and functional movement patterns.
Conclusion
By incorporating these top upper body exercises into your workout routine, you can build strength, muscle mass, and overall fitness. Whether aiming for muscle growth, strength gains, or improved performance, these exercises offer versatility and effectiveness for achieving your goals.
What Type Of Exercise Is Best For Mental Health?
In Ancient Greece, 500 years before the time of Jesus Christ, a brilliant thinker named Thales of Miletus championed the concept of a “sound mind, in a sound body.” This ancient wisdom emphasized the importance of nurturing both mental and physical well-being.
Fast forward to the present day, and we find ourselves rediscovering this timeless wisdom. It’s becoming increasingly evident that good mental health is just as crucial as physical fitness. Therefore, crafting a comprehensive self-care routine is essential. Think of it as assembling your personal toolbox for a healthy life, with exercise standing out as one of the most effective tools for optimizing mental health.
Why Does Exercise Benefit Mental Health?
Physical exercise offers a plethora of mental health benefits. Consider the sense of well-being experienced after a brisk walk. This feeling arises from intriguing physiological processes that occur in the body during movement. According to Harvard Health, aerobic exercises such as running or swimming act as natural stress relievers.
During periods of stress, the body releases chemicals like adrenaline and cortisol to boost energy levels. However, an excess of these chemicals can lead to feelings of jitteriness and tension. Aerobic exercise helps restore balance by reducing the production of these stress chemicals while simultaneously increasing blood flow, delivering oxygen throughout the body. This oxygen boost also triggers the release of endorphins, which act as tiny messengers of happiness and relaxation in the brain, contributing to the post-workout euphoria.
Resistance training can also alleviate anxiety. As Sergii Putsov, a professional athlete, coach, and author, explains:
“Training is one of the best ways to get yourself back to feeling the best you possibly can. Not only does it allow you to spike dopamine when you lift weights, but your confidence will naturally grow as you see your body change every day.”
In addition to the neurochemical benefits of physical activity, it can also enhance self-confidence in various ways. Consistent exercise builds discipline, a sense of accomplishment, and self-trust, which can serve as motivation in other areas of life.
While regular exercise offers numerous documented benefits for mental health, it’s essential to acknowledge its limitations. Conditions like major depressive disorder and chronic anxiety often require a comprehensive treatment approach, which may include counseling, therapy, medication, and, in severe cases, inpatient treatment at a mental health facility.
The Best Exercises for Mental Health
Fortunately, there’s a wide range of exercises that can trigger a dopamine boost, and some may even provide an additional testosterone kick in men. For simplicity, we’ll focus on exercises identified by researchers as particularly effective to get you started. Remember, the goal is to establish a sustainable routine before gradually increasing intensity.
Low-Intensity Aerobic Exercises
Embarking on an exercise regimen doesn’t have to be daunting. Low-intensity aerobic exercises offer an excellent entry point, requiring minimal equipment and providing ample flexibility. Activities like brisk walking, jogging in place, or even dancing can be seamlessly incorporated into daily life, regardless of location.
Focusing on bodyweight exercises such as squats and lunges allows for a straightforward yet effective home-based routine. As fitness levels and confidence grow, one can explore the broader array of equipment and options available at a gym.
Success lies in finding activities that are genuinely enjoyable and can be consistently integrated into one’s schedule. Research consistently demonstrates the significant benefits of low-intensity exercise, with just 30-35 minutes, 3-5 times a week, being sufficient to boost confidence and improve various aspects of life.
Outdoor Exercises
Exercising outdoors is another fantastic way to enhance mental health. Beginning with brisk walks and gradually incorporating jogging or running not only helps manage weight but also enhances blood circulation throughout the body.
As comfort with walking increases, one can transition to a gentle jog or incorporate more intense running sessions. The overarching objective is to stimulate the release of dopamine, leading to remarkable improvements in mood and overall well-being. Outdoor exercise also promotes better sleep quality.
Group Exercises
Feeling stressed, isolated, or lacking motivation? Group exercise could be the unexpected solution. Beyond the well-documented physical benefits, group workouts offer a significant boost to mental well-being. The social connection forged with fellow fitness enthusiasts counteracts the loneliness prevalent in our increasingly digital world. Shared workout experiences foster camaraderie and a sense of belonging, leaving participants feeling more connected and supported. Moreover, the group atmosphere injects an element of fun into the fitness routine, replacing gym anxiety with laughter and mutual encouragement.
This social aspect also enhances motivation. Exercising alongside others creates a sense of accountability, inspiring individuals to push themselves further. Supporting each other’s efforts and celebrating milestones together cultivates a strong sense of connection and accomplishment, encouraging continued commitment to overall well-being.
Strength Training
Strength training offers benefits beyond building muscle mass. Each successful repetition represents a small victory, chipping away at stress and self-doubt. Witnessing physical strength increase fosters empowerment and resilience, making daunting challenges seem more manageable. This newfound confidence spills over into other aspects of life, instilling a sense of capability and readiness to confront obstacles.
Strength training also positively impacts mood by triggering the release of endorphins, the brain’s natural stress relievers. These chemicals alleviate anxieties and promote feelings of positivity and optimism. Furthermore, the focus and determination required during strength training sessions serve as a form of mental meditation, temporarily alleviating worries and fostering a clear, present mindset.
Conclusion
The evidence is clear: exercise is not only beneficial for physical health but also a powerful tool for enhancing mental well-being. Various forms of exercise offer opportunities to get started, and committing to a regular exercise routine could potentially transform one’s state of mind. Exploring different exercise modalities and finding those best suited to individual preferences and needs is both enjoyable and rewarding. If motivation is lacking, consider seeking support through a free consultation to kickstart your wellness journey.